Table of Contents
- Understanding HIPAA Breach Notification Rules
- Components of the Breach Notification Rules
- Timelines and Methods of Notification
- Penalties for Non-Compliance
- The Importance of Adhering to Notification Rules
- Key Components of the Notification Rules
- Steps to Take in the Event of a Breach
- Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding HIPAA Breach Notification Rules
In recent years, safeguarding sensitive patient information has become paramount in the healthcare sector. Understanding HIPAA breach notification rules is vital for healthcare providers to maintain trust and adhere to legal obligations. This guide delves deep into the intricacies of notification rules, helping you stay compliant and informed.
What are HIPAA Breach Notification Rules?
HIPAA, which stands for the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, was enacted in 1996 to define and implement national standards that protect sensitive patient health information from being disclosed without the patient’s consent or knowledge. Central to this protection initiative are the HIPAA Breach Notification Rules, which enforce stringent guidelines to maintain trust and transparency in healthcare dealings. This section takes a deeper look at what these rules entail and why they hold an indispensable position in healthcare compliance.
Definition and Importance
The HIPAA Breach Notification Rules refer to a set of guidelines that dictate how healthcare organizations and associated entities should handle data breaches concerning protected health information (PHI). Essentially, these rules foster a culture of responsibility and vigilance, ensuring that patients are promptly informed when there is unauthorized access to or disclosure of their information.
It is pivotal for healthcare institutions to internalize and adhere to these rules to avoid substantial fines and legal repercussions, and equally to foster trust with their patient base. Let’s delve deeper into various facets of these notification rules.
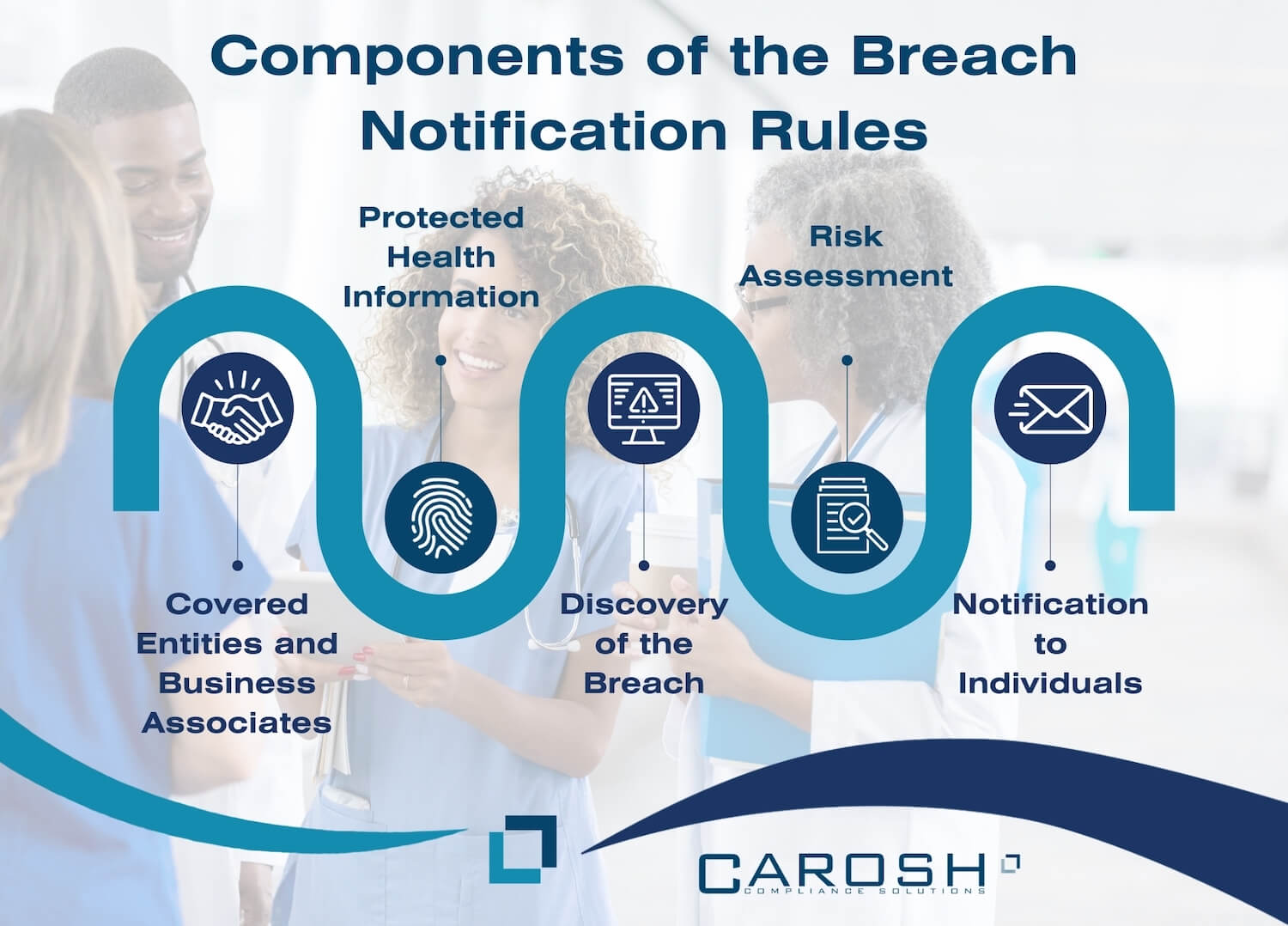
Components of the Breach Notification Rules
Understanding the HIPAA Breach Notification Rules is a multi-faceted process involving several crucial components. Here are the key aspects:
- Covered Entities and Business Associates: The rules apply to covered entities, which include healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearinghouses, and business associates who have access to PHI through services provided to the covered entities.
- Protected Health Information (PHI): This involves a deep understanding of what constitutes PHI, including all individually identifiable health information held or transmitted by a covered entity or its business associate.
- Discovery of the Breach: The rules outline the systematic procedure that healthcare entities should follow upon discovering a breach of unsecured PHI.
- Risk Assessment: After identifying a potential breach, entities are required to perform a risk assessment to ascertain the probability of PHI being compromised.
- Notification to Individuals: In case of a breach, timely notification to affected individuals is mandatory. The notification, which must be issued without unreasonable delays, outlines the nature of the breach and the steps individuals should take to protect themselves.
Timelines and Methods of Notification
- Immediate Response: A defining feature of the rules is the emphasis on an immediate response to limit potential damage, including initiating investigations and mitigating the breach’s effects.
- Notification Period: The affected entities have a period of 60 days from the discovery of the breach to notify the individuals affected, the HHS, and in some cases, the media.
- Methods of Notification: Notifications can be sent out through various methods, including written notices, emails (if the individual has agreed to receive such notifications), and, in urgent situations, through phone calls.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Breaching the rules can lead to severe repercussions including:
- Civil Penalties: These could range from financial fines to more punitive measures depending on the severity of the breach.
- Criminal Penalties: In severe cases, criminal charges can be brought against entities, including imprisonment.
Understanding the HIPAA Breach Notification Rules is not just a legal necessity but a moral imperative in the healthcare industry. Contact Carosh Compliance Solutions for professional help. These rules champion transparency and foster a trust-based relationship between healthcare providers and patients, thereby playing a monumental role in securing sensitive health information.
Through rigorous adherence to these rules, healthcare entities can foster a safer, more secure environment, shielding both patients and themselves from the repercussions of data breaches while demonstrating a steadfast commitment to ethical practices. It’s a testimony to a healthcare institution’s dedication to preserving the sanctity of patient information and fostering a reputation of reliability and trustworthiness in the volatile landscape of health information security.
The Importance of Adhering to Notification Rules
In a world that is becoming increasingly digitalized, data breaches have regrettably become a somewhat common event. The healthcare industry is no exception to this; it harbors a significant amount of sensitive information, thus making it a lucrative target for cybercriminals. In such a precarious landscape, adhering to the HIPAA breach notification rules not only acts as a safeguard for individual data but also serves as a beacon of trust and a measure of the quality of healthcare organizations. Let us unpack the critical reasons that underscore the importance of adhering to these notification rules.
Building Patient Trust
- Transparent Communication: In the wake of a data breach, healthcare entities have a golden opportunity to maintain, and even bolster, trust through transparent communication. The notification rules mandate that individuals be informed promptly, allowing organizations to control the narrative and demonstrate responsibility.
- Preservation of Patient Relationships: Upholding the notification rules is a direct testament to an organization’s commitment to its patients. It fosters a relationship based on trust and openness, where patients feel valued and protected.
- Empowering Patients: By promptly informing patients about a data breach, organizations empower them with the information needed to take protective actions, such as monitoring their accounts or changing passwords, thereby reducing potential harm and reinforcing trust.
Legal Compliance
- Avoidance of Penalties: Adherence to the notification rules is not just morally right but also a legal imperative. Compliance helps in avoiding substantial fines that regulatory bodies may impose, and which can range vastly depending on the severity of the breach.
- Preventing Legal Battles: Strict adherence to the rules can protect organizations from legal entanglements that not only consume time and resources but can have long-standing repercussions on the functioning and reputation of the entity.
- Maintaining Regulatory Relationships: Being in compliance with the rules portrays the organization as a responsible entity in the eyes of regulatory bodies, fostering a healthy working relationship that can be beneficial in the long run.
Maintaining Reputation
- Mitigating Reputation Damage: In an industry where reputation is integral to success, following the prescribed protocols can help mitigate the damage to an organization’s standing. It portrays the entity as one that takes its duties seriously and upholds the highest standards of integrity and professionalism.
- Business Continuity: Adherence to the rules ensures that the organization can continue its operations without facing shutdowns or restrictions, which regulatory bodies might impose due to non-compliance.
- Public Perception: Upholding the rules shapes positive public perception, showcasing the organization’s steadfast commitment to protecting individual data and standing tall as a reliable and trustworthy entity in the healthcare industry.
The HIPAA breach notification rules play a pivotal role in steering the healthcare entities through the troubled waters that data breaches invariably create. By fostering trust through transparency, steering clear of legal repercussions, and maintaining a stalwart reputation, adherence to these rules emerges not merely as a compliance requirement but a cornerstone for success in the digital era of the healthcare industry. It underlines a commitment to ethical conduct, empathy towards patients, and a conscious effort towards maintaining the sanctity of the sacred provider-patient relationship.
Key Components of the Notification Rules
Understanding the intricate components of the notification rules is essential in establishing a robust healthcare compliance strategy. Here, we delve into the key aspects that define these rules.
Individual Notification
Under the HIPAA breach notification rules, covered entities are obligated to notify affected individuals promptly, generally within 60 days of discovering the breach. Notifications must include:
- A description of the breach
- The types of information that were involved
- Steps individuals should take to protect themselves
- A brief overview of what the covered entity is doing to investigate the breach, mitigate harm, and prevent further breaches
Media Notification
In cases where the breach affects more than 500 residents of a State or jurisdiction, the covered entity must notify prominent media outlets serving the area. This notification should be issued concurrently with the individual notifications.
Notification to the Secretary
HIPAA breach notification rules also dictate the timely notification to the Secretary of the U.S Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Depending on the number of individuals affected, this notification can have different timelines:
- For breaches affecting 500 or more individuals: The notification should be made concurrently with individual notifications.
- For breaches affecting fewer than 500 individuals: The covered entity can maintain a log of the breaches and submit it annually to the HHS.
Web Notifications
In addition to the above notifications, covered entities must also post a notice of the breach on their home page for a period of 90 days or provide an alternative means of notice as outlined in the HIPAA regulations.
Steps to Take in the Event of a Breach
In the unfortunate event of a data breach, here is a structured guideline to adhere to:
- Identify and Contain the Breach: As soon as a breach is detected, the primary step is to contain it and prevent further data loss.
- Notification to Individuals: Prompt notification to affected individuals, including the necessary details as stipulated under the notification rules, is essential.
- Engage Legal and Public Relations Teams: Leveraging the expertise of legal and PR teams can help in crafting appropriate responses and managing the aftermath effectively.
- Notification to the Secretary and Media: Depending on the severity of the breach, notifications to the secretary and media outlets should be undertaken as per HIPAA guidelines.
- Review and Strengthen Security Measures: Post a breach, it’s vital to review existing security protocols and bolster them to prevent future breaches.
Conclusion
In a landscape where the sanctity of personal data is ever so critical, understanding and complying with HIPAA breach notification rules stands central. Through adherence to these norms, healthcare providers can navigate the complex terrains of data security, nurturing trust and ensuring the wellbeing of their patients. Carosh Compliance Solutions is able to help make sure covered entities are prepared, and protected as best as possible from HIPAA violations.
Frequently Asked Questions
In the complex world of healthcare data security, questions abound about the specific rules and regulations surrounding HIPAA breach notifications. Here, we delve into some of the most frequently asked questions to provide you with a detailed understanding in a conversational manner.
What qualifies as a breach under the HIPAA?
A HIPAA breach includs, but not limited to, unauthorized access to patient files, sharing PHI without patient consent, or the accidental sending of PHI to the wrong individual. However, it’s worth noting that not all violations are considered breaches; for a situation to qualify as a breach, it must involve the exposure of PHI in a manner that leads to a significant risk of financial, reputational, or other harm to the individual affected.
What is considered “unsecured protected health information?”
“Unsecured protected health information” is a term used to describe PHI that is not rendered unusable, unreadable, or indecipherable to unauthorized individuals through a technology or methodology specified by the Secretary of Health and Human Services. Essentially, it refers to information that is not secured through a means that meets the standards established in the guidance issued by the Secretary.
What are the timelines for notifying the different entities post a breach?
The timelines to adhere to post a breach are indeed quite structured. Upon discovering a breach of unsecured PHI:
- Individual Notifications: Affected individuals must be notified without unreasonable delay, and in any case, not later than 60 days following the discovery of a breach. Notifications should be thorough, including a description of the breach, the type of information compromised, and steps individuals should take to protect themselves.
- Media and Secretary Notifications: If the breach involves more than 500 residents of a State or jurisdiction, then the media must be notified, as well as the Secretary of Health and Human Services, contemporaneously with the individual notifications. For breaches affecting fewer than 500 individuals, the covered entity may log the breach and report it to the Secretary annually.
- Notification by Business Associates: In cases where a breach occurs at a business associate’s end, they are required to notify the covered entity without undue delay, and no later than 60 days from the discovery of the breach.
What repercussions can organizations face for non-compliance?
Non-compliance with HIPAA rules can lead to a range of repercussions, both legal and reputational. On the legal front, organizations can face civil money penalties ranging from $100 to $50,000 or more per violation, with a maximum annual penalty of $1.5 million.




