Table of Contents
Key Aspects of PHI under HIPAA
In the complex landscape of healthcare information, Protected Health Information (PHI) stands at the heart of privacy and security concerns. Under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), safeguarding PHI is not just a regulatory requirement, but a measure taken to protect patient privacy and maintain trust in the healthcare system. This article delves into the intricacies of PHI, offering insights into what constitutes PHI, the importance of its protection, and examples that illustrate its scope within the realm of HIPAA compliance.
Key Aspects of PHI under HIPAA
Protected Health Information (PHI) under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) encompasses a broad spectrum of information that is needed for the privacy and security framework within healthcare. PHI is essentially any information found in an individual’s medical records or payment history that could be used to identify them. This definition extends beyond straightforward identifiers such as names and Social Security numbers to include any data that, especially when combined with other information, might reveal a person’s identity. The examples of PHI underline the comprehensive approach HIPAA takes to protect patient privacy, emphasizing that even seemingly innocuous pieces of information could lead to identification when pieced together.

Expansive Coverage of PHI Under HIPAA
Moreover, the realm of PHI is not confined to electronic records alone. In acknowledging the diverse modes through which healthcare information is recorded and communicated, HIPAA’s protection of PHI spans across electronic, physical, and oral formats. This inclusive approach ensures that all forms of patient information, whether stored in a digital health record, written on paper, or spoken during a consultation, receive the same level of protection under the law.
Regulatory Measures to Safeguard PHI
To safeguard this wide-ranging category of information, HIPAA has instituted rigorous regulations governing the use and disclosure of PHI. These rules mandate that healthcare providers and their business associates enact robust safeguards to preserve the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of PHI. Such measures are designed to prevent unauthorized access to or disclosure of patient information, thereby ensuring that PHI is used and shared responsibly and only for legitimate purposes. The regulations compel covered entities to not only protect PHI but also to actively manage its security through ongoing risk assessments, employee training, and the implementation of physical, technical, and administrative safeguards.
Comprehensive Protection of Health Information
In essence, the key aspects of PHI under HIPAA highlight the act’s thorough protection mechanisms tailored to the diverse and potentially identifiable nature of health information. By encompassing both electronic and non-electronic forms of PHI and mandating strict use and disclosure protections, HIPAA aims to maintain a high standard of privacy and security in the healthcare sector, ensuring that individuals’ health information is handled with the utmost care and respect.
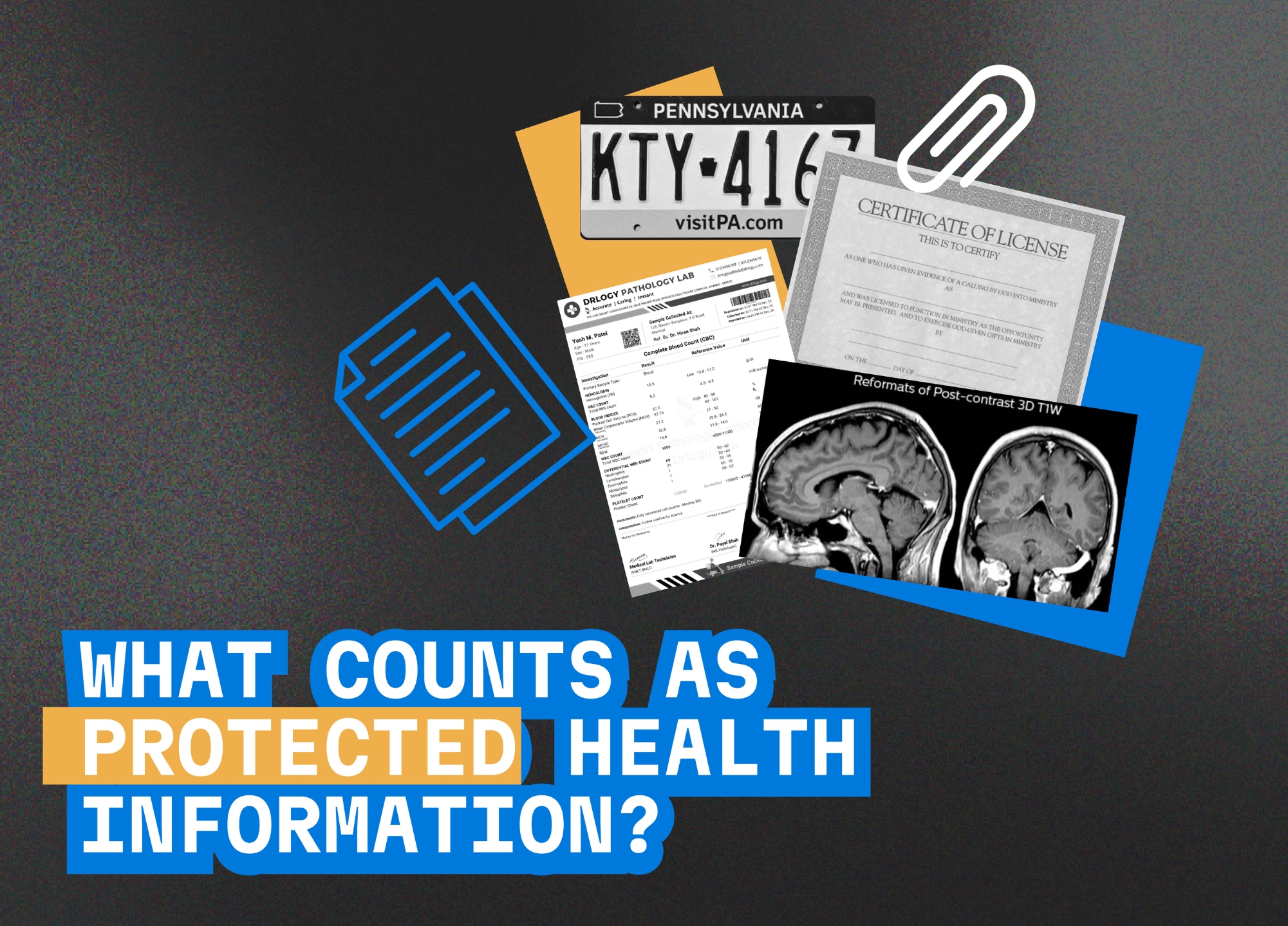
Examples of PHI
Protected Health Information (PHI) under HIPAA encompasses a wide array of data types that, when pieced together, can reveal the identity of an individual along with details about their health status, medical treatment, or payment for healthcare services. Examples of PHI highlight the diverse nature of data that healthcare providers, insurers, and their business associates must protect to ensure patient privacy and comply with HIPAA regulations.

Comprehensive Nature of Medical Records as PHI
Medical records stand as a primary category of Protected Health Information (PHI), containing comprehensive details about a patient’s medical history, diagnoses, treatments, and prognosis. These records are a compilation of various forms of documentation, including physicians’ notes, laboratory test results, imaging studies, and prescriptions. They serve as a cornerstone in the continuum of care, providing healthcare professionals with the information necessary to make informed treatment decisions.
Financial Details Embedded in PHI
Billing information also constitutes PHI, encapsulating the financial transactions related to healthcare services. This includes account numbers, detailed charges for services provided, insurance information, and payment histories. Such information not only relates to the financial aspects of healthcare but also includes enough detail to identify patients and link them to specific healthcare services.
Importance of Demographic Information
Demographic information, often collected at the time of registration or initial consultation, includes data such as names, addresses, dates of birth, Social Security numbers, phone numbers, and email addresses. This category of PHI is crucial for identifying patients within the healthcare system and facilitating communication but also poses a risk if not properly safeguarded.
Imaging and Lab Results as PHI
Imaging studies and laboratory test results, such as X-rays, MRI scans, and blood tests, provide visual or quantitative insights into a patient’s health condition. When these images and results are identifiable to an individual, they become a form of PHI, necessitating protection under HIPAA.
Appointment Details as Part of PHI
Appointment information, which includes the dates and times of medical appointments, the nature of these appointments, and any follow-up instructions or notes, also falls under the umbrella of PHI when it can be linked to a specific patient. This information, while seemingly administrative, can reveal details about a patient’s health concerns or conditions.
Communication as PHI
Finally, emails or other forms of written communication between a healthcare provider and a patient that contain identifiable health information are considered PHI. Whether it’s a simple appointment reminder or a detailed discussion about treatment options, if the communication includes identifiable health information, it must be protected in accordance with HIPAA regulations.
Summary of PHI under HIPAA
In summary, the examples of PHI illustrate the breadth of information covered under HIPAA, from clinical data found in medical records and test results to administrative details in billing and appointment schedules, as well as personal communications between providers and patients. Ensuring the privacy and security of this diverse set of information is fundamental to maintaining pat
Importance of Protecting PHI
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) plays a crucial role in the healthcare sector by mandating stringent protection measures for Protected Health Information (PHI) to uphold patient privacy and sustain trust within the healthcare system. The significance of these regulations stems from the potential repercussions that unauthorized access, use, or disclosure of PHI can have on individuals. Such breaches can lead to severe consequences, including invasions of privacy, instances of discrimination, and considerable financial losses, all of which can undermine the foundational trust patients place in healthcare entities.
HIPAA’s Protective Framework for PHI
To mitigate risks and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of Protected Health Information (PHI), HIPAA introduces comprehensive Privacy and Security Rules. These regulations are crafted to guide healthcare organizations and their business associates towards a proactive approach in safeguarding sensitive health information. A cornerstone of these regulations is the mandate for conducting thorough risk assessments. These assessments are crucial in identifying potential vulnerabilities in an organization’s handling of PHI, enabling the development of targeted strategies to address these risks effectively.
Implementation of Robust Safeguards
Moreover, HIPAA regulations stress the importance of implementing robust physical and electronic safeguards. These measures are diverse and designed to secure physical access to facilities where PHI is stored and to deploy advanced encryption techniques to protect electronic data from cyber threats. The aim is to establish a secure environment that minimally risks unauthorized access to PHI.
Crucial Role of Staff Training
Staff training also constitutes an essential component of HIPAA’s protective measures. Through regular and comprehensive training programs, employees of healthcare organizations learn about the significance of PHI protection and the specific practices they must adhere to ensure compliance with HIPAA rules. This training is instrumental in fostering a culture of privacy and security awareness within all organizational levels.
Establishing Policies and Procedures
Furthermore, establishing clear policies and procedures for managing and securing PHI is a fundamental requirement under HIPAA. These policies and procedures provide a formal framework for the consistent and effective handling of PHI, detailing protocols for access, use, disclosure, and transmission of sensitive information. They act as a reference point for employees, ensuring that every action taken concerning PHI aligns with the organization’s commitment to privacy and the legal requirements set by HIPAA.
Summary of HIPAA’s Comprehensive Approach
In essence, HIPAA’s comprehensive approach through the Privacy and Security Rules underscores the utmost importance of maintaining patient privacy and trust within the healthcare system. By adhering to these guidelines and implementing necessary risk assessments, safeguards, training, and policies, healthcare organizations and their business associates can significantly reduce the risks associated with handling PHI. This concerted effort not only protects individuals’ well-being and privacy but also reinforces the integrity of the healthcare system as a whole.

Protected Health Information is the cornerstone of patient privacy and a pivotal aspect of healthcare compliance. Understanding and properly managing PHI is essential for healthcare providers and their business associates to protect patient privacy, comply with HIPAA regulations, and foster a trustworthy healthcare environment. As healthcare continues to evolve with technology, so too does the importance of diligently protecting PHI against emerging threats. By familiarizing ourselves with the principles of PHI, we contribute to a more secure and confidential healthcare system.
Q&A
Q: What exactly is Protected Health Information (PHI)?
A: PHI refers to any health-related information that can identify an individual, including medical records, billing information, and any personal details related to healthcare services.
Q: Why is it important to protect PHI?
A: Protecting PHI is crucial for maintaining patient confidentiality, preventing identity theft, and ensuring trust in the healthcare system. It’s also a legal requirement under HIPAA.
Q: Can you give examples of PHI?
A: Examples include medical records, billing details, demographic information like names and addresses, test results, and any part of a patient’s medical history or payment records.
Q: How do healthcare providers and their associates protect PHI?
A: They implement safeguards as mandated by HIPAA, including physical, administrative, and technical protections, to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of PHI.




